Looking for Help with Assignments?
-RUCats has 80 hours of tutoring available online and in-person. Check the tutoring tab in Canvas!-Instructors and Lead TAs have a combined 10 hours of Office Hours, open to all sections. See times/locations here.
-Piazza (found in the Canvas sidebar) provides fast support from Course Staff and other Students. Be sure to search to see if someone has asked a similar question!
-If you need a computer to complete work on, iLab machines can be found in the CSL (Hill 252) and surrounding rooms.
ER Triage - 20 Course Points
The purpose of this assignment is to implement a Priority Queue, creating a min heap data structure and using an array to store the elements of the min heap.
You can download and submit the project files via Autolab.
Refer to our Programming Assignments FAQ for instructions on how to install VSCode, how to use the command line and how to submit your assignments.
See this video on how to import the project into VSCode and how to submit into Autolab.
The assignment has one component:
Coding (20 points) submitted through Autolab.
Overview
You have just been assigned the task of assisting the fictional Rutgers University Hospital in triaging patients based off of their consciousness level in their Emergency Department. For simplicity, you will only be using The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) which assigns patients a number from 3 to 15 based on their level of consciousness. The GCS number assigned to the patient will also correspond to a color (seen in the Driver):
3 to 8 – RED
9 to 13 – ORANGE
14 – YELLOW
15 – GREEN
The lower the GCS, the more prioritized the patient is, hence a priority queue data structure will be used which processes patients based on their priority rather than following the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle of a regular queue.
In this lab, you must fill in the code for insert(), swim(), sink() and deleteMin() methods to fully enable the functionality of the Priority Queue ER Triage driver visualization.
Implementation
Overview of files provided
- Driver.java, a visual driver class which simulates the Emergency Room Priority Queue, requires text based input to create a Patient object and using a button to add a Patient and to remove a Patient. The driver will call ERTriage.java to perform these methods. Do not submit to Autolab.
- ERTriage.java, Contains Priority Queue methods which you will write: insert(), swim(), sink(), and deleteMin(). This will be submitted to Autolab.
- Attributes:
ER: Patient[] – array structure which refers to the ER of a hospital containing Patient objects. Index 0 will always remain empty and no Patient objects should be added to this index. Thus, the root of the min heap should always be at Index 1 of the array.
totalPatients: int – The number of patients in the array structure. Make sure to update correctly when adding or removing patients.
SIZE: int – fixed number of slots of the initial array declaration.
- Attributes:
- Patient.java, holds the attributes specific to each Patient object such as their name and GCS number. Do not submit to Autolab.
- Comparison methods:
compareTo(): compares the GCS number of the patient first, in the case of equal GCS numbers, the names are compared.
equals(): uses both patient name and GCS number to determine equality of Patient objects.
Getter and setter methods are also provided.
- Comparison methods:
- The TestERTriage.java class in the test/ directory is used to test your methods using JUnit. Feel free to edit this file, as it is provided only to help you test your code. It is not submitted, and it is not used to grade your code. Do not submit to Autolab.
UPDATE and SUBMIT the ERTriage.java file to Autolab
Implementation Notes
DO NOT add any instance variables to the ERTriage class
DO NOT add any public methods to the ERTriage class
DO NOT change the headers of ANY of the given functions
DO NOT add any import statements
DO NOT change the class name
DO NOT use System.exit()
Programming
To complete this lab, you will implement the insert(), deleteMin(), sink(), and swim() methods shown below.
To Run: run the following commands from the innermost ERTriage directory, containing the src and bin folders.
- Compile:
- Windows: javac -d bin -cp “lib/cs112.jar” src/triage/*.java
- Mac/Linux: javac -d bin -cp lib/cs112.jar src/triage/*.java
- Run:
- Windows: java -cp “bin;lib/cs112.jar” triage.Driver
- Mac/Linux: java -cp bin:lib/cs112.jar triage.Driver
Ensure that you are working in the correct directory. See this image:

resize() [PROVIDED]
This method resizes the min heap array structure by doubling the length of the array. You will call this method in your insert() method.
exch(int x, int y) [PROVIDED]
This method exchanges the position of two Patients in the ER array structure by taking in the two respective indices for the Patients as parameters. You will call this method in your sink() and swim() methods.
Methods to be implemented by you:
1. insert(String name, int GCS)
This method takes the name of the Patient and their GCS level, then using this information you will create a Patient object and add it to the first open spot in the ER array structure. From here, you call swim() to fix the ordering of the min heap structure. You MAY allow duplicates.
You should check if you need to resize before you insert the Patient. Additionally, increment totalPatients before you call swim().
Note: remember, we leave index 0 as null when working with an array-based heap representation.
2. swim(int current)
This method makes sure that when a Patient is added, the heap order is not violated and the ER array maintains its min heap structure. The added patient will be “swimmed up” through the heap as needed. Use the Patient compareTo() method to compare two Patients. Call exch() to swap two patients within the priority queue, if the parent is greater than the child.
View the Priority Queue lecture slides (slide 18) for more information on implementing swim(). You may have to adapt the code to be a min heap representation instead.
3. deleteMin()
This method will get the patient with the lowest GCS score (at the top of the heap). After storing that patient, replace it with the last patient in the array. Update totalPatients, then call sink() on the root of the tree. Return the Patient object that is going to be seen next (the one you removed).
If there are no patients in the array, return null instead.
4. sink(int current)
Ensure that when a Patient is deleted the heap order is not violated. By implementing this operation, the Patient that we swapped into index 1 will sink down the structure as needed. The Patient must be sunk so that the min heap order is maintained. Use the Patient compareTo() method to compare two Patients. Call exch() to swap two patients within the priority queue, if the parent is greater than the child. If both children are the exact same, then swap with the left child.
View the Priority Queue lecture slides (slide 20) for more information on implementing sink(). You may have to adapt the code to be a min heap representation instead.
Driver
Once you implement your code, you can run the Driver.java file and interact with the driver. It will show a visualization of an array with an empty index 0, with buttons and text fields to add the patient’s information and add the patient to the priority queue, as well as remove the most urgent patient.
You can use this Driver to test your code, but it is still useful to write JUnit test cases, in case the driver does not catch all cases.
Here is an example of a min heap with the insertion of the following patients, their names and corresponding GCS number in the visual driver:
Meredith Grey 10, Mark Sloan 6, Alex Karev 14, Derek Shepherd 3, Cristina Yang 8
The array structure of the min heap is visualized in the center, index 0 will never be used and is always empty. The array structure is scrollable, a scroll bar is provided above the “REMOVE” button. More indices of the array become visible:
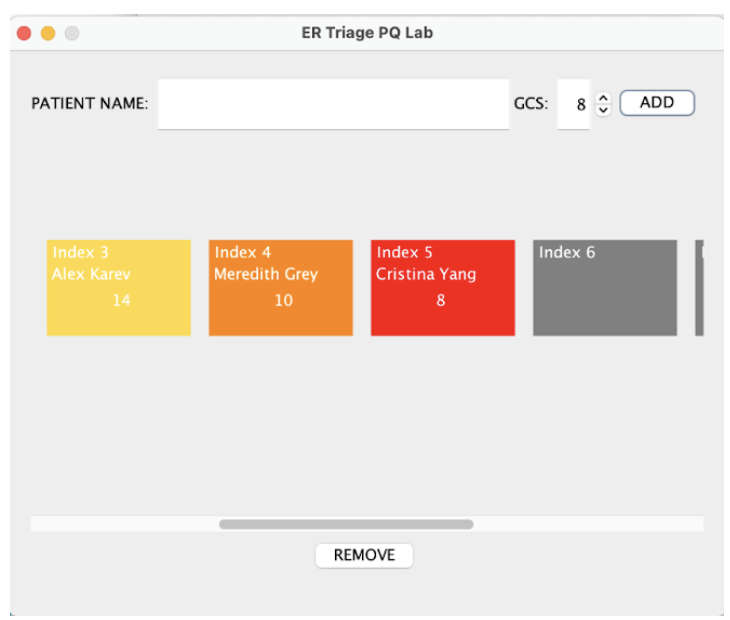
Executing and Debugging
- Use the run option in VS Code to run this program – right click ERTriage.java and select Run Java. You could also use compile commands:
Compile:
- Windows: javac -d bin -cp “lib/cs112.jar” src/triage/*.java
- Mac/Linux: javac -d bin -cp lib/cs112.jar src/triage/*.java
Run:
- Windows: java -cp “bin;lib/cs112.jar” triage.Driver
- Mac/Linux: java -cp bin:lib/cs112.jar triage.Driver
In VS Code, ensure that you have the INNERMOST ERTriage open by doing File > Open Folder and opening the folder labeled ERTriage.
Writing JUnit Tests
You do not have to submit this, this is for you to test your own code.
In the main project folder, there exists a “test” folder next to the “src” folder. This contains a JUnit test class, which can run and test pieces of your code. To compile and run these tests, you must install the Test Runner extension. See the Programming FAQ for more info on VS Code extensions.
The two tests are for testInsert() and testDeleteMin(), and you can fill these tests in. Once you do, remove the fail() statements at the bottom and run.
You are provided with a premade JUnit test class for ERTriage. You can finish writing the test methods, by using JUnit test methods (such as assertTrue(), assertFalse(), assertEquals()) in order to test your code.
Tests not running?
First, make sure you’re in the right folder and the tests are implemented. Next, if you have the “Code Runner for Java” or Oracle “Java” extension, make sure you uninstall those extensions. Remember that you fill in the tests for testInsert() and testDeleteMin().
VSCode Extensions
You can install VSCode extension packs for Java. Take a look at this tutorial. We suggest:
Importing VSCode Project
Download ERTriage.zip from Autolab Attachments.
Unzip the file by double clicking.
Open VSCode
Import the folder to a workspace through File > Open Folder
Executing and Debugging
You can run your program through VSCode or you can use the Terminal to compile and execute. We suggest running through VSCode because it will give you the option to debug.
You can hit the triangle “Run Java” button at the top of the Driver.java class, or right click on Driver.java and select “Run Java”
NOTE: if you have ERTriage (2) -> ERTriage or CS112 -> ERTriage in VS Code, open the INNERMOST ERTriage through File -> Open Folder.
Before submission
REMOVE all print statements you have written in ERTriage.java
Collaboration policy. Read our collaboration policy on the course syllabus.
Submitting the assignment. Submit ERTriage.java separately via the web submission system called Autolab. To do this, go to Autolab and find the correct assignment and submit your Java file.
Getting help
If anything is unclear, don’t hesitate to drop by office hours or post a question on Piazza.
- Find instructors and Lead TAs office hours here
- Find tutors office hours on Canvas -> Tutoring
- In addition to office hours we have the Coding and Social Lounge (CSL), a community space staffed with student community managers which are undergraduate students further along the CS major to answer questions.
By Alexandra Domanski and Christian Parra

